

Creating a coveted “dream team” is the goal of any organization—members who mesh effortlessly, are highly productive, and can work through any challenge. If we’re lucky, we end up on these magical teams a handful of times over our careers. But the reality is that it’s not luck or magic. There’s a science behind high-performing teams, and understanding key principles helps leaders to build these teams again and again.
Dr. Bruce Tuckman’s research has been the foundation of understanding groups for the past 60 years. Tuckman found that groups or teams develop through five distinct stages:
In recent years, researchers have found that today’s workplaces have fewer complete endings, with the final stage often signaling an expansion of projects and integration of new team members. Most of today’s teams are in a perpetual cycle of forming-storming-norming, rarely if ever getting to the performing stage. As a result, teams cannot easily get to effective collaboration or engage in true innovation.
The first key to high-performing teams is to allow them to authentically move through every stage. The best teams intentionally think about how to onboard and integrate new members, and allow time for the group to acclimate to one another, while also engaging in team-building and team-training to accelerate the group’s development.
While the five stages paint a picture of a relatively smooth, linear process toward high performance, the reality is that teams can, and often do struggle. In recent years, Greg Giesen and Lauri Osborne discovered that the storming phase establishes either good norms (like transparency, respect, and inclusion) or bad norms (like cliques or conflict avoidance/false harmony).
Good norms set the group on the path toward high performance while bad norms cause the group to veer off to dysfunction. While a group can recover from bad norming, it takes focused and intentional effort on the part of the leader to move the group into new patterns of engagement and interaction. This becomes harder the longer the group is permitted to stay in bad norming, as patterns become habitualized, and even lead to a psychological state known as learned helplessness, where people just give up.
Dysfunction cripples teams in every industry. Patrick Lencioni, a leading expert on teams, identified five common dysfunctions in his book, The Five Dysfunctions of a Team. They are:
Teams that experience even one of these dysfunctions are at risk for failing to accomplish their goals. And since dysfunctions can cascade, it is common for teams to experience several at the same time, and even all five. This leads to disengagement and even attrition of your best people. One study found that 30% of employees have left a job due to a negative team environment.
"As teams work together, they are asked to move back and forth on a continuum between coordination, cooperation, and collaboration. These words are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct types of teamwork.
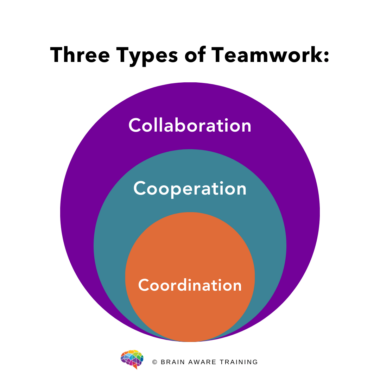
Let’s look at the definitions and differences:
While coordination only requires basic communication and planning skills (which many people still struggle with), cooperation requires a clear process for execution and accountability. Collaboration requires the most advanced skills of all: building trust, engaging in creativity, innovation, and having a mindful process for resolving the inevitable conflicts that arise from this most complex form of work.
Some teams may only operate in one or two zones on a daily basis, but more and more, teams must move across the levels seamlessly throughout the week.
The best team leaders empower team members to perform at their best. They articulate clear expectations for the type of teamwork required and ensure that members have the skills and resources to succeed. In addition, they have what is called collaborative intelligence (CQ)—the ability to think with others and value the diverse ways people frame questions, process information, and innovate new ideas.
However, most organizations don’t offer the right training to help teams develop the skills they need to perform successfully—or promote the people who do have these skills. More often, leaders are chosen because they were excellent performers as individual contributors. Research shows that the best individual performers often don’t make effective team leaders because they inevitably and unconsciously use the team to execute their own vision rather than harnessing the strengths of others.
It’s vital that organizations choose team leaders based on their skills for creating the environment for others to excel and collaborate. This includes helping others develop trust, engage with respect, resolve conflict, and wrestle with the often challenging work of creativity and innovation. In addition, they must invest in developing future team leaders by training on these learnable skills
As Dr. Dawna Markova and Angie McArthur, authors of Collaborative Intelligence: Thinking with People Who Think Differently state,
“Leaders who understand and maximize the different ways that people process information are more prepared to inspire, empower, and meld the diverse intellectual assets within their organizations.”
Effective team leaders know they have a responsibility to create the environment and conditions for a diverse group of members to come together to do the difficult but rewarding work of collaboration.
When the above strategies are implemented, organizations can create the conditions high-performing teams need to form, develop, and thrive in the workplace. Good teams might fall into place by luck but truly excellent teams are a result of intentional strategy, ongoing support, and targeted development.